Science 101: Digestive enzymes for FODMAPs
A review on who can benefit and how to help patients get started

An overview on who can benefit and how to help patients get started
Endogenous & exogenous enzymes
For many with FODMAP sensitivities the amount of digestive enzymes produced by the body is not enough to break down all the FODMAPs in their diet.
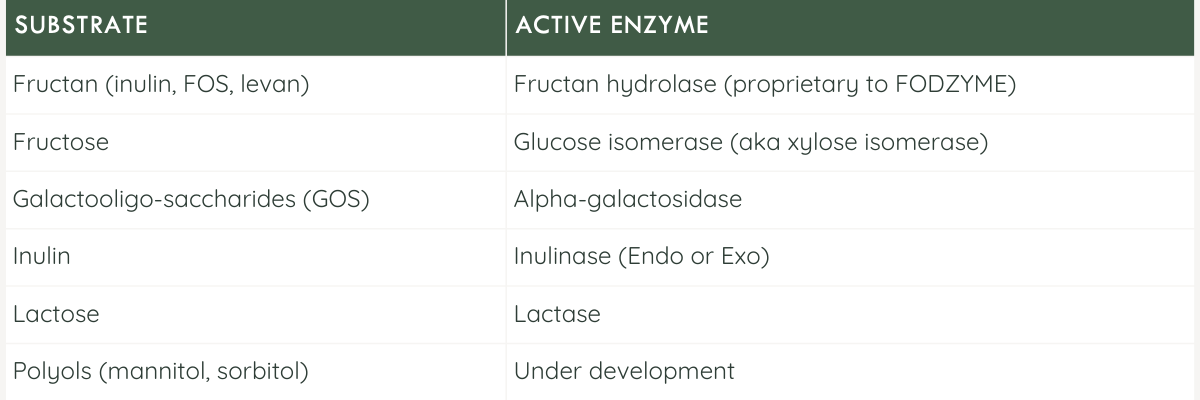
The body does not naturally produce any enzyme to sufficiently break down fructans or galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS). Furthermore, the amount of lactase produced by the body is not always enough to control symptoms.
Digestive enzymes targeted at FODMAPs
Only about 5-15% of dietary fructans are absorbed; the rest are excreted or fermented by bacteria in the colon, which can lead to the hallmark symptoms of gas, bloating and other digestive troubles [1]. Fructans are suggested as the most common symptom-triggering FODMAP [2].
Digestive enzymes act on the food, not the body. They help break down FODMAPs before they get fermented by bacteria and draw water into the colon.
Supporting research
Use of digestive enzymes has proven successful at reducing abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence and diarrhea [3,4].
FODZYME's digestive enzyme blend is formulated to target the broadest spectrum of FODMAP carbohydrates possible and those that are most commonly triggering.
FODZYME’s powder formulation maximizes homogenization of enzymes with food and thus the availability of enzymes to break down gut triggers before gastric pepsin and other proteases can threaten enzyme stability [5]. This means FODZYME is more effective than capsules, which slow down the assimilation of enzymes with food.

FODZYME digestive enzyme blend
FODZYME's efficacy at breaking down FODMAPs has been verified through SHIME, a scientifically validated model of a human digestive tract [6].
Peer-reviewed research confirmed 90% of a typical dose of fructan was degraded within half an hour and 70% of fructose was absorbed during the simulated small intestinal transit, thus reducing gas production.
Research also confirmed SCFA production was reduced but not depleted, indicating FODZYME’s enzymatic approach may be favorable to overall colonic health than avoiding FODMAPs [6].
Use FODZYME to help patients achieve relief from chronic gut distress.
Gut Questions?
Head to the healthcare section of our FAQs to learn more about FODZYME & our Partner's Program.
Download patient handouts, watch one of our free CEU webinars or just say hi 👋
References
[1] Fedewa A, Rao SS. Dietary fructose intolerance, fructan intolerance and FODMAPs. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2014;16(1):370. doi:10.1007/s11894-013-0370-0
[2] Eswaran S, Singh P, Rifkin S, et al. ARE ALL FODMAPS CREATED EQUAL? A BLINDED, RANDOMIZED REINTRODUCTION TRIAL TO DETERMINE WHICH FODMAPS DRIVE CLINICAL RESPONSE IN IBS PATIENTS. Gastroenterology 2021;160:S-745.
[3] Di Stefano M, Miceli E, Gotti S, et al. The Effect of Oral α-Galactosidase on Intestinal Gas Production and Gas-Related Symptoms. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 2007;52:78-83.
[4] Tuck CJ, Taylor KM, Gibson PR, Barrett JS, Muir JG. Increasing Symptoms in Irritable Bowel Symptoms With Ingestion of Galacto-Oligosaccharides Are Mitigated by α-Galactosidase Treatment. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113(1):124-134.
[5] Piper, D. W.; Fenton, B. H. pH stability and activity curves of pepsin with special reference to their clinical importance. Gut 1965, 6 (5), 506–508. DOI: 10.1136/ gut.6.5.506.
[6] Ochoa KC, Samant S, Liu A, Duysburgh C, Marzorati M, Singh P, Hachuel D, Chey W, Wallach T. In-Vitro Efficacy of Targeted FODMAP Enzymatic Digestion (FODZYME®) in a High-Fidelity Simulated Gastrointestinal Environment. Gastro Hep Advances.

